In the world of bowling, there’s a key factor that determines the performance of a bowling ball: its RG, or Radius of Gyration. Now, you might be wondering, what exactly is RG and why is it so important? Well, let us enlighten you. RG refers to the distance from the center of a bowling ball to its outer edge – essentially, how the mass is distributed within the ball. This might seem like a technical detail, but understanding the significance of RG can make a world of difference in improving your game on the lanes. So, grab your bowling shoes and join us as we explore the important role RG plays in the world of bowling balls.
Review contents
Understanding Radius of Gyration (RG)
Definition of RG
Radius of Gyration (RG) in bowling balls refers to the measure of how weight is distributed within the ball. It is the distance at which the mass of the ball is concentrated, and it plays a crucial role in determining the ball’s overall motion on the lane. RG is typically measured in inches and is a significant aspect to consider when choosing a bowling ball.
Importance of RG in Bowling Balls
Radius of Gyration is a vital factor in understanding a bowling ball’s behavior and performance on the lane. The RG value affects various aspects such as the ball’s rolling motion, skid phase, hook phase, and back-end reaction. It is essential to comprehend the impact of RG to make informed decisions about ball selection, customization, and optimizing playstyle.
Factors Affecting RG
Density of the Core Material
The density of the core material is one crucial factor that influences the RG of a bowling ball. Generally, higher-density core materials, such as those found in heavy oil balls, tend to have lower RG values. On the other hand, lower-density core materials, commonly seen in high-performance or pearl bowling balls, result in higher RG values. This distinction in density affects how the mass is distributed within the ball, consequently influencing its overall motion.
Core Shape and Symmetry
The shape and symmetry of the core design significantly impact the RG of a bowling ball. Different core shapes, such as symmetrical, asymmetrical, or pancake, have varying RG values. Symmetrical cores often have higher RG values, leading to smoother and more controllable ball motion. Asymmetrical cores, on the other hand, typically exhibit lower RG values, resulting in stronger back-end reactions and increased angularity.
Mass Distribution within the Core
The distribution of mass within the core plays a vital role in determining the RG of a bowling ball. Varying mass distribution affects the differential and flare potential of the ball, which in turn affects ball motion. By altering the mass distribution within the core, manufacturers can precisely control the RG to achieve specific performance characteristics. Consequently, understanding the mass distribution within the core allows bowlers to choose the most suitable bowling ball for their playing style and lane conditions.
Effect of RG on Ball Motion
Rolling Motion of the Bowling Ball
The RG value directly influences the rolling motion of a bowling ball. A higher RG causes the ball to roll earlier and exhibit a smoother, more controlled motion on the lane. Conversely, a lower RG promotes a later roll with increased skid and a stronger back-end reaction. This distinction in rolling motion is crucial in adjusting to different lane conditions and optimizing one’s shot-making strategy.
Skid Phase
During the skid phase, the RG of the bowling ball plays a significant role in determining how quickly it transitions from skid to hook. A higher RG ball will tend to transition earlier, providing more overall hook potential. In contrast, a lower RG ball will have an extended skid phase before transitioning, potentially offering more length on drier lane conditions.
Hook Phase
The RG of a bowling ball also impacts the hook phase, where the ball transitions from skid to a hooked motion. A higher RG generally promotes a smoother and more gradual hook, making it easier to control. On the other hand, a lower RG results in a quicker, sharper hook, which can be advantageous in heavier oil patterns or when needing a more aggressive reaction.
Back-End Reaction
The RG value influences the back-end reaction, which refers to the ball’s motion towards the pins after the hook phase. Higher RG balls tend to provide a smoother and more predictable backend reaction, which can be beneficial for bowlers seeking consistency. Conversely, lower RG balls tend to exhibit a stronger, more angular back-end reaction, generating more pin action and potential for higher scores.
Choosing the Right RG
Matching RG to Lane Conditions
Selecting the appropriate RG for the lane conditions is crucial for optimizing performance. On heavy oil patterns, where an early roll is desired, a lower RG ball is preferred. This allows the ball to pick up traction sooner and combat the oil. In contrast, on drier lane conditions where length and more back-end reaction are essential, a higher RG ball will provide the best results. Matching the RG to the lane conditions ensures the ball has the right characteristics to maximize one’s scoring potential.
Preferred Playing Style
Bowlers with different playing styles may find certain RG values more suitable for their needs. Players who prefer a smooth, controlled motion may opt for higher RG balls, while those seeking a more aggressive and angular motion may lean towards lower RG balls. Understanding one’s preferred playing style and the RG’s impact is crucial in selecting the perfect bowling ball to enhance performance.
Type of Shot
The specific shot a bowler intends to execute also influences the RG selection. For straighter shots or spares, a higher RG ball may be preferred as it offers predictability and consistency. However, for players who rely on hook shots or need a stronger angular motion to get around corner pins, a lower RG ball may be the ideal choice. Considering the type of shot one intends to throw allows for better decision-making when it comes to selecting bowling balls.
Differential and RG
Understanding Differential
Differential is another critical factor to consider when discussing RG and ball motion. Differential refers to the difference between the ball’s RG axis and its PSA (Preferred Spin Axis) axis. It affects the ball’s flare potential, which influences the amount of track flare and hook potential. Higher differentials result in increased track flare and hook potential, while lower differentials lead to less flare and a smoother overall motion.
How Differential and RG Work Together
Differential and RG work together to determine a bowling ball’s overall motion and flare potential. By adjusting the differential and RG values, manufacturers can manipulate a ball’s reaction to suit specific lane conditions and player preferences. High RG and low differential balls typically offer smoother, more controlled motions, while low RG and high differential balls provide more aggressive hook potential. Understanding the interplay between these two factors is crucial in optimizing ball performance.
RG Variations in Different Bowling Balls
High RG Balls
High RG bowling balls typically exhibit smoother, more controlled motions with slightly longer skid phases. They are suitable for heavy oil patterns and bowlers who prefer a slower, more controlled hook. High RG balls allow for easier length and predictability, making them ideal for bowlers who value consistency and shot repeatability.
Low RG Balls
Low RG bowling balls tend to provide stronger back-end reactions, sharper hooks, and quicker transitions from skid to hook. These balls are well-suited for medium or dry lane conditions where length and strong angular motion are desired. Bowlers who prefer aggressive reactions or rely on a more powerful hook will find low RG balls to be an excellent choice.
Medium RG Balls
Medium RG bowling balls strike a balance between high and low RG balls, offering a versatile performance on a variety of lane conditions. They provide a moderate hook potential, controlled motion, and a balanced skid-to-hook transition. Medium RG balls are popular among bowlers who seek adaptability and the ability to adjust to changing lane conditions.
The Evolution of RG in Bowling Balls
Historical Impact of RG
The understanding and implementation of RG in bowling balls have significantly influenced the sport over the years. In the past, limited knowledge about RG and its effects resulted in simpler core designs with less control over ball motion. As bowlers and ball manufacturers gained more insights into RG, they began developing advanced core designs and materials to optimize performance based on different lane conditions and player preferences.
Advancements in Science and Technology
The advancements in science and technology played a crucial role in furthering the understanding of RG and its impact on bowling ball performance. Through extensive research and testing, manufacturers have been able to fine-tune core designs, analyze mass distribution, and create innovative materials. This enhanced knowledge, combined with computer simulations and advanced manufacturing processes, has revolutionized the bowling industry and improved the overall performance of bowling balls.
Current Trends and Innovations
In recent years, the focus on RG continues to shape the development of bowling balls. Manufacturers constantly strive to improve the RG values, core designs, and materials to create more versatile and high-performing products. The ongoing advancements in understanding RG, combined with technological innovations, have led to balls with greater predictability, improved control, and enhanced pin carry, enhancing the overall bowling experience.
Customizing RG
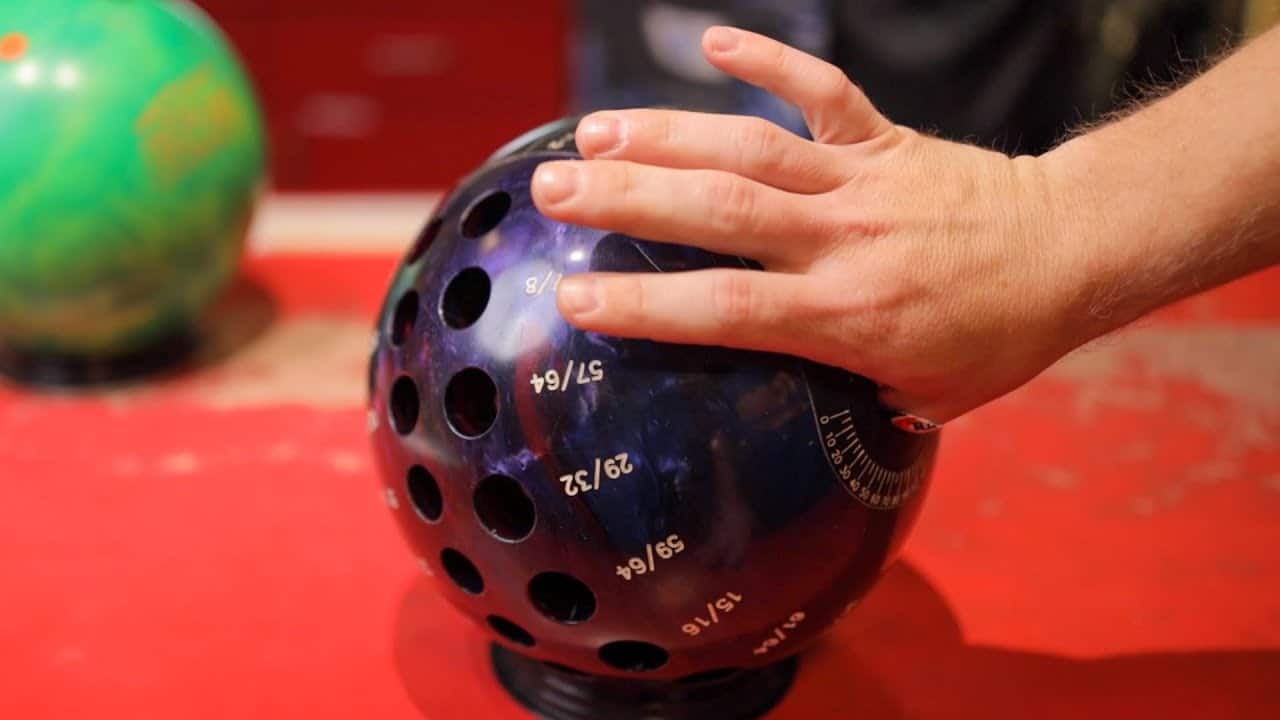
Drilling Techniques
Drilling techniques play a significant role in customizing the RG of a bowling ball. By strategically positioning the finger and thumb holes, pro shop professionals can alter the ball’s mass distribution and thus its RG values. These adjustments cater to the specific requirements of individual bowlers, allowing them to fine-tune the ball’s performance to their liking and adapt to different lane conditions.
Balance Hole Placement
Balance hole placement is another method employed to customize the RG of a bowling ball. By drilling a balance hole in a specific location, pro shop professionals can adjust the weight distribution within the ball, ultimately affecting its RG values. This customization allows bowlers to fine-tune the ball’s reaction and tailor it to their unique preferences and playing style.
RG-Altering Inserts
RG-altering inserts are specialized inserts that can be placed inside the finger or thumb holes of a bowling ball, offering additional customization options. These inserts feature various shapes and sizes, allowing bowlers to further manipulate the ball’s RG by adjusting the mass distribution. The ability to alter the RG through inserts provides bowlers with even more control and flexibility in optimizing their ball’s performance.
The Future of RG
Research and Development
Ongoing research and development efforts in the bowling industry are likely to further enhance our understanding of RG and its impact. By delving deeper into the intricate dynamics of ball motion and utilizing advanced technologies, manufacturers will continue to explore new avenues to optimize RG values and core designs. The insights gained from these endeavors will contribute to the creation of bowling balls with superior performance characteristics.
Potential Improvements in Ball Performance
As our understanding of RG and its influence on ball motion continues to expand, future bowling balls are expected to exhibit even greater performance capabilities. Improved RG control, advanced core designs, and innovative materials will offer bowlers an unprecedented level of customization and adaptability. These advancements will enhance the overall bowling experience, elevating the sport to new levels of excitement and achievement.
Conclusion
Final Thoughts on RG
Radius of Gyration (RG) is a critical factor in understanding the behavior and performance of bowling balls. It influences the ball’s rolling motion, skid phase, hook phase, and back-end reaction. By comprehending the impact of RG, bowlers can make informed decisions regarding ball selection, customization, and playstyle optimization. Matching the RG to the lane conditions, considering one’s playing style and shot type, and understanding the interplay between RG and differential are essential in maximizing ball performance.
Continued Importance in Bowling
With ongoing research, advancements in science and technology, and a focus on RG, the importance of understanding and utilizing RG in bowling balls will only continue to grow. The ability to customize RG through drilling techniques, balance hole placement, and RG-altering inserts empowers bowlers to tailor their equipment for optimal performance. As the future unfolds, the continued refinement of RG values, core designs, and materials will undoubtedly pave the way for enhanced ball performance and further enjoyment of the dynamic sport of bowling.




![Spare bowling ball Top 10 in 2024. (reviews) Top 10 Best Spare Bowling Balls [2021 Reviewed]](http://landofbowling.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/Top-10-Best-Spare-Bowling-Balls-2021-Reviewed.jpg)