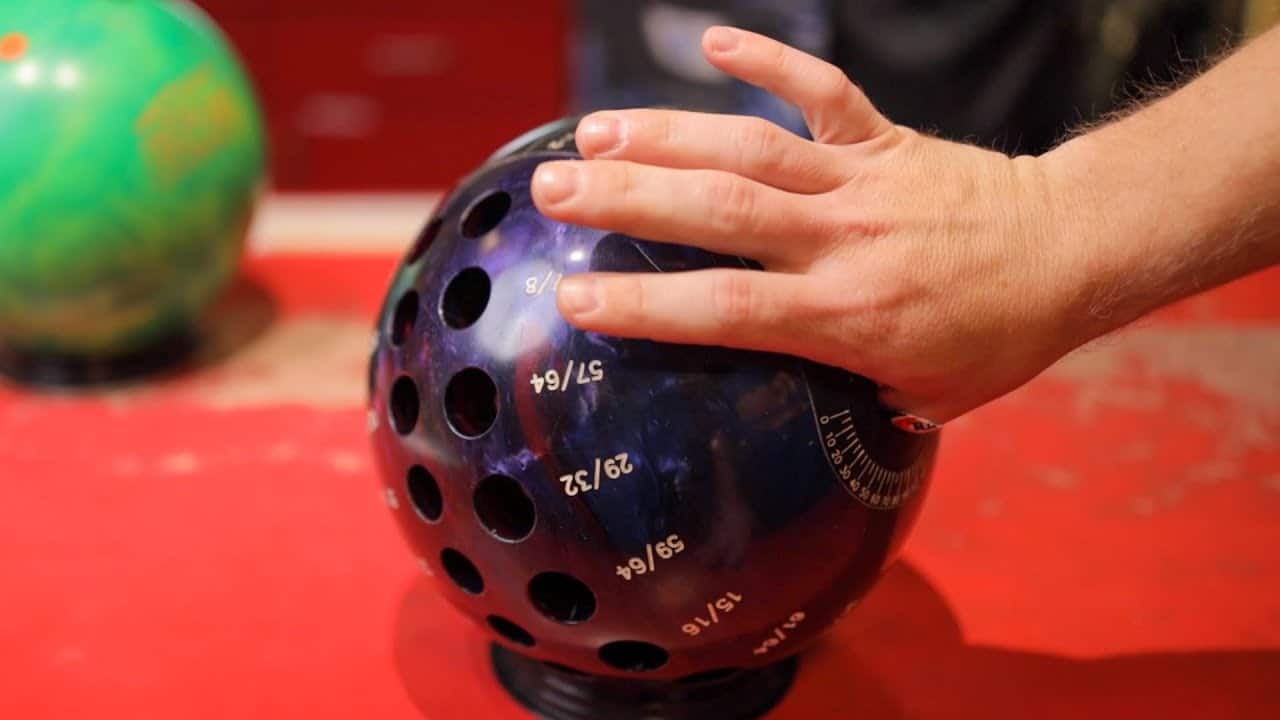
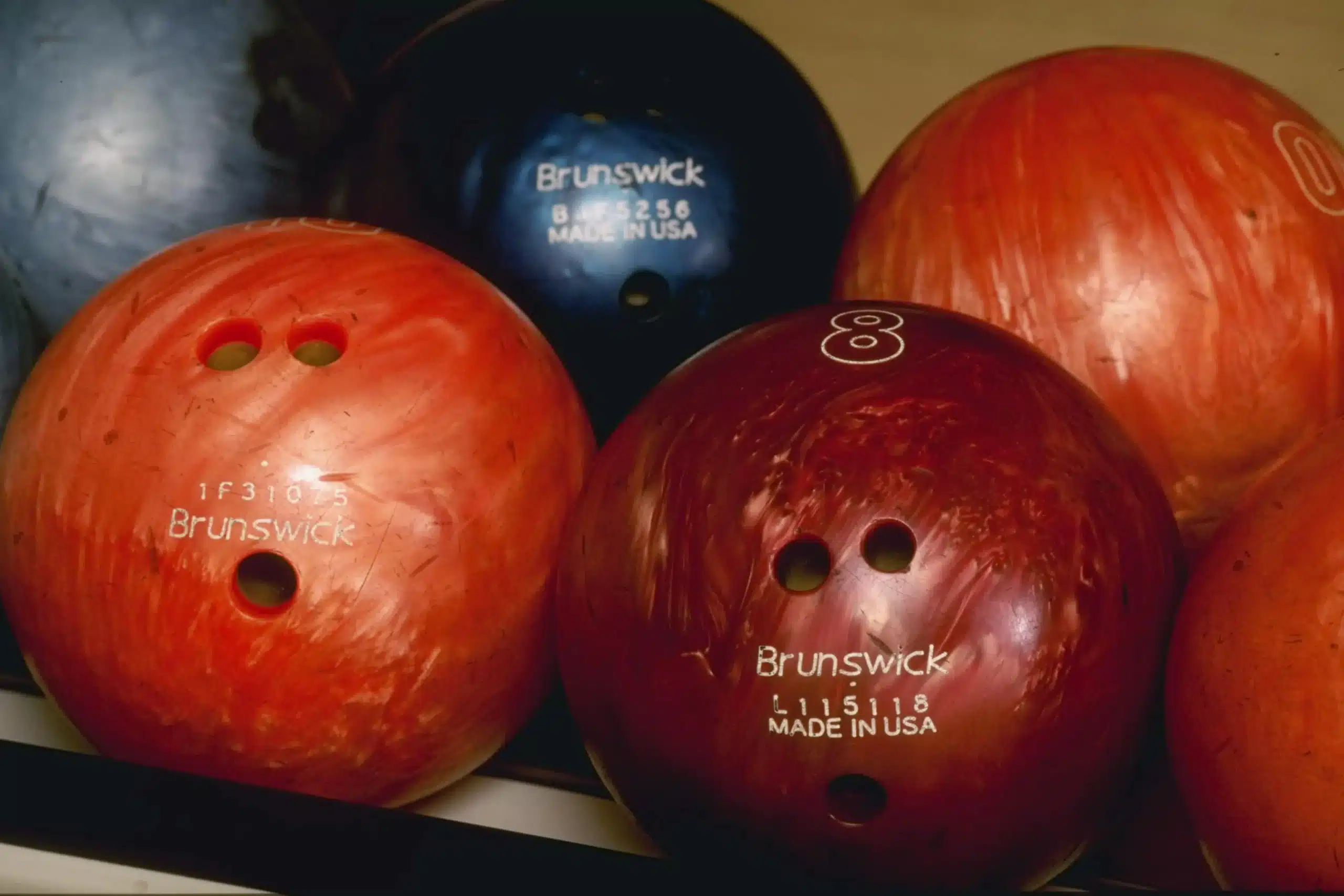
Step up to the lane and prepare to be bowled over by our fascinating exploration into the world of bowling balls. Ever wondered how many finger holes these spherical wonders possess? Prepare to have your curiosity satisfied as we delve into this puzzling question. So grab your favorite snack, put on your best bowling shoes, and join us on this journey as we uncover the answer to the age-old question: how many finger holes does a bowling ball have?
This image is property of cdn.shopify.com.
Review contents
Types of Bowling Balls
Plastic Bowling Balls
Plastic bowling balls are the most basic and least expensive type of bowling ball. They are made from polyester or plastic materials and are typically solid in color. Plastic bowling balls are ideal for beginners or casual bowlers who value affordability over performance. However, they lack the hook potential of more advanced bowling ball types.
Urethane Bowling Balls
Urethane bowling balls are a step up from plastic balls and offer more hook potential. They have a higher friction surface, allowing for better control and hooking action. Urethane balls are popular among intermediate bowlers who want to improve their game without investing in more expensive options.
Reactive Resin Bowling Balls
Reactive resin bowling balls are designed for advanced bowlers who want maximum hook potential and performance. These balls have a porous outer shell that racts to the friction on the lane, resulting in a strong hooking motion. Reactive resin balls provide greater pin action and carry, making them a popular choice for competitive bowlers.
Particle Bowling Balls
Particle bowling balls combine reactive resin with microscopic particles to increase friction and hook potential. These balls are designed for experienced bowlers who want even more hook and control on oily lanes. Particle bowling balls offer a unique blend of power and aggressiveness.
Hybrid Bowling Balls
Hybrid bowling balls incorporate both reactive resin and particle additives to provide a balanced combination of hook potential and control. They are versatile and can be used on a variety of lane conditions, making them a popular choice among bowlers who want adaptability without sacrificing performance.
Standard Finger Hole Layout
Three Holes Layout
The most common finger hole layout in bowling balls is the three holes layout. This layout consists of two finger holes and one thumb hole. The finger holes are drilled equidistant from each other, with the thumb hole positioned slightly offset from the finger holes. The three holes layout provides a balanced grip and allows for a comfortable release.
Two Holes Layout
The two holes layout, as the name suggests, features two finger holes and no thumb hole. This layout is often used by bowlers who prefer a two-handed throwing technique. The absence of a thumb hole allows for greater flexibility in gripping and releasing the ball.
Fingertip Grip Layout
The fingertip grip layout is a variation of the three holes layout, but with a key difference. In this layout, the finger holes are drilled slightly larger and deeper, allowing for a grip where only the fingertips are inserted into the ball. The fingertip grip provides more control and a greater ability to generate a hooking motion.
Conventional Grip Layout
The conventional grip layout is similar to the fingertip grip, but with one notable distinction. In this layout, the finger holes are drilled smaller, resulting in a deeper insertion of the fingers. The conventional grip provides a firm and secure hold on the ball, making it suitable for bowlers who prefer a more traditional grip style.
Single Thumb Hole Design
One-Handed Thumb Release
The one-handed thumb release is the most common method used by bowlers who bowl with one hand. In this technique, the thumb is the first to be released from the ball during the forward swing. This release style offers precision and control, allowing the bowler to accurately target their shots.
Two-Handed Thumb Release
The two-handed thumb release is a technique used by bowlers who bowl with both hands. In this technique, the thumb is released simultaneously with the other hand, resulting in a powerful and explosive throw. This release style is popular among bowlers who seek maximum hook potential and pin carry.
Finger Hole Sizes
Standard Finger Hole Sizes
Standard finger hole sizes are determined by the diameter of the bowler’s fingers. There are generally four standard sizes available, ranging from small to large. The finger holes should be drilled to ensure a snug and secure fit for the fingers, providing optimal control and comfort.
Custom Finger Hole Sizes
For bowlers with non-standard finger sizes, custom finger holes can be drilled to accommodate their unique needs. Custom finger hole sizes provide a personalized fit, ensuring maximum control and comfort while bowling. It is recommended to consult with a professional ball driller to determine the appropriate custom finger hole sizes.
This image is property of bowlingforbeginners.com.
Finger Hole Placement
Symmetrical Finger Hole Layout
In a symmetrical finger hole layout, the finger holes are positioned equidistant from the center of the bowling ball. This layout provides a balanced weight distribution, ensuring the ball rolls smoothly and evenly down the lane. Symmetrical finger hole placement is commonly used in traditional three-holes layouts.
Asymmetrical Finger Hole Layout
As the name suggests, an asymmetrical finger hole layout involves positioning the finger holes at varying distances from the ball’s center. This layout allows bowlers to fine-tune the ball’s weight distribution, achieving desired ball reaction and hook potential.
Benefits of Finger Holes
Enhanced Control
Finger holes play a crucial role in providing bowlers with enhanced control over their throws. The grip provided by the finger holes helps the bowler maintain a firm hold on the ball, resulting in greater accuracy and consistency.
Better Grip
Finger holes allow bowlers to grip the ball securely, preventing slippage during the release. A proper grip ensures that the ball can be held comfortably and confidently, improving overall performance on the lane.
Increased Rev Rate
Rev rate refers to the number of revolutions the ball makes as it rolls down the lane. Finger holes allow bowlers to exert more force on the ball, generating increased rev rates. A higher rev rate can lead to greater hook potential and pin carry.
Improved Ball Reaction
The placement and size of finger holes can affect the ball’s reaction on the lane. A well-fitted finger hole layout can optimize the ball’s performance, ensuring the desired hooking action and pin carry.
This image is property of d2culxnxbccemt.cloudfront.net.
Custom Finger Hole Options
Oval Finger Holes
Oval finger holes are a custom finger hole option that provides a more ergonomic grip. They are shaped to match the contours of the bowler’s fingers, reducing finger fatigue and providing a comfortable fit. Oval finger holes offer improved control and accuracy.
Finger Inserts
Finger inserts are removable attachments that can be inserted into the finger holes. They provide additional customization options for bowlers, allowing them to fine-tune the fit and feel of the ball. Finger inserts also offer added comfort and can reduce stress on the fingers during prolonged bowling sessions.
Number of Finger Holes
Traditional Three Holes Layout
The traditional three holes layout is the most common configuration, featuring two finger holes and one thumb hole. This layout is widely used by bowlers of all skill levels and offers a balanced grip and control.
Two Holes Layout
The two holes layout is an alternative to the traditional three holes layout. It consists of two finger holes, with no thumb hole. This layout is often preferred by two-handed bowlers or those who use a no-thumb delivery technique.
Extra Finger Holes
Some bowlers may opt for additional finger holes to suit their specific needs and preferences. Extra finger holes can be added to accommodate a particular gripping style or to achieve a desired ball reaction. Custom requests should be made to a professional ball driller to ensure proper hole placement and functionality.
This image is property of photos.demandstudios.com.
Finger Hole Maintenance
Regular Cleaning and Polishing
To maintain optimal performance, it is important to regularly clean and polish the finger holes of the bowling ball. This helps remove debris, oils, and sweat that can accumulate over time and affect the grip. Using a quality ball cleaner and a soft cloth, gently clean the finger holes after each bowling session to keep them in top condition.
Replacing Worn-out Grips
Over time, the finger holes of a bowling ball may wear out or become damaged. When this happens, it is crucial to replace the worn-out grips to maintain a proper grip and control. Seek professional assistance to have the worn-out grips carefully removed and replaced with new ones for optimal performance.
Finger Hole Plugging and Redrilling
Reasons for Plugging and Redrilling
There are instances where bowlers may need to plug and redrill their finger holes. This is usually done to correct grip or fit issues, change finger hole sizes, or alter the finger hole layout. Plugging and redrilling involves filling the existing finger holes and then drilling new ones according to the desired specifications.
Professional Assistance Required
Plugging and redrilling finger holes should only be done by a professional ball driller. It requires expertise and specialized equipment to ensure the proper alignment and functionality of the new finger holes. Professional assistance is essential to avoid damaging the bowling ball and to achieve the desired results.
In conclusion, finger holes in bowling balls play a crucial role in a bowler’s performance and control. The type and layout of finger holes, as well as their maintenance, can significantly impact the overall bowling experience. Whether using a standard layout or opting for custom finger holes, it is important to find the right fit and grip to enhance accuracy, consistency, and enjoyment while bowling.
This image is property of bowlingforbeginners.com.









![Spare bowling ball Top 10 in 2024. (reviews) Top 10 Best Spare Bowling Balls [2021 Reviewed]](http://landofbowling.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/Top-10-Best-Spare-Bowling-Balls-2021-Reviewed.jpg)